One of the six basic groups of animals—along with reptiles, mammals, amphibians, fish, and protozoa—birds are characterized by feathers and (in most species) the ability to fly. Below you will discover 10 important facts about birds.

Surprisingly, for those of us proud of our mammalian heritage, there are twice as many species of birds as there are species of mammals—about 10,000 and 5,000 species, respectively, worldwide. gender. By far the most common type of bird is the “sparrow” or perching bird, which is characterized by its grip on tree branches and its tendency to sing. Other notable bird orders include “Gruiformes” (cranes and rails), “Cuculiformes” (cuckoos), and “Columbiformes” (pigeons and doves), among about 20 other taxa.

Naturalists divide the class of birds, Greek name “ aves ,” into two subclasses: “ paleognathae ” and “ neognathae .” Curiously, Paleaeognathae , or “old jaws,” includes birds that first evolved during the Cenozoic Era, after the extinction of the dinosaurs—primarily birds like ostriches, emus, and kiwis. Neognathae , or “new jaws,” may have originated further back in the Mesozoic Era and included all other types of birds, including the birds mentioned in slide #2. (Most Paleognathae are completely flightless, with the exception of the Tinamou of Central and South America.)

The main groups of animals can often be distinguished by their skin: furry animals, scaly fish, arthropods with exoskeletons, and feathered birds. You might imagine that birds evolved feathers to fly, but you would be wrong on two counts: first, the ancestors of birds, the dinosaurs, evolved feathers first, and second, feathers apparently evolved evolved primarily as a means of conserving body heat, and were only secondarily selected by evolution to enable the first primitive birds to take to the air.
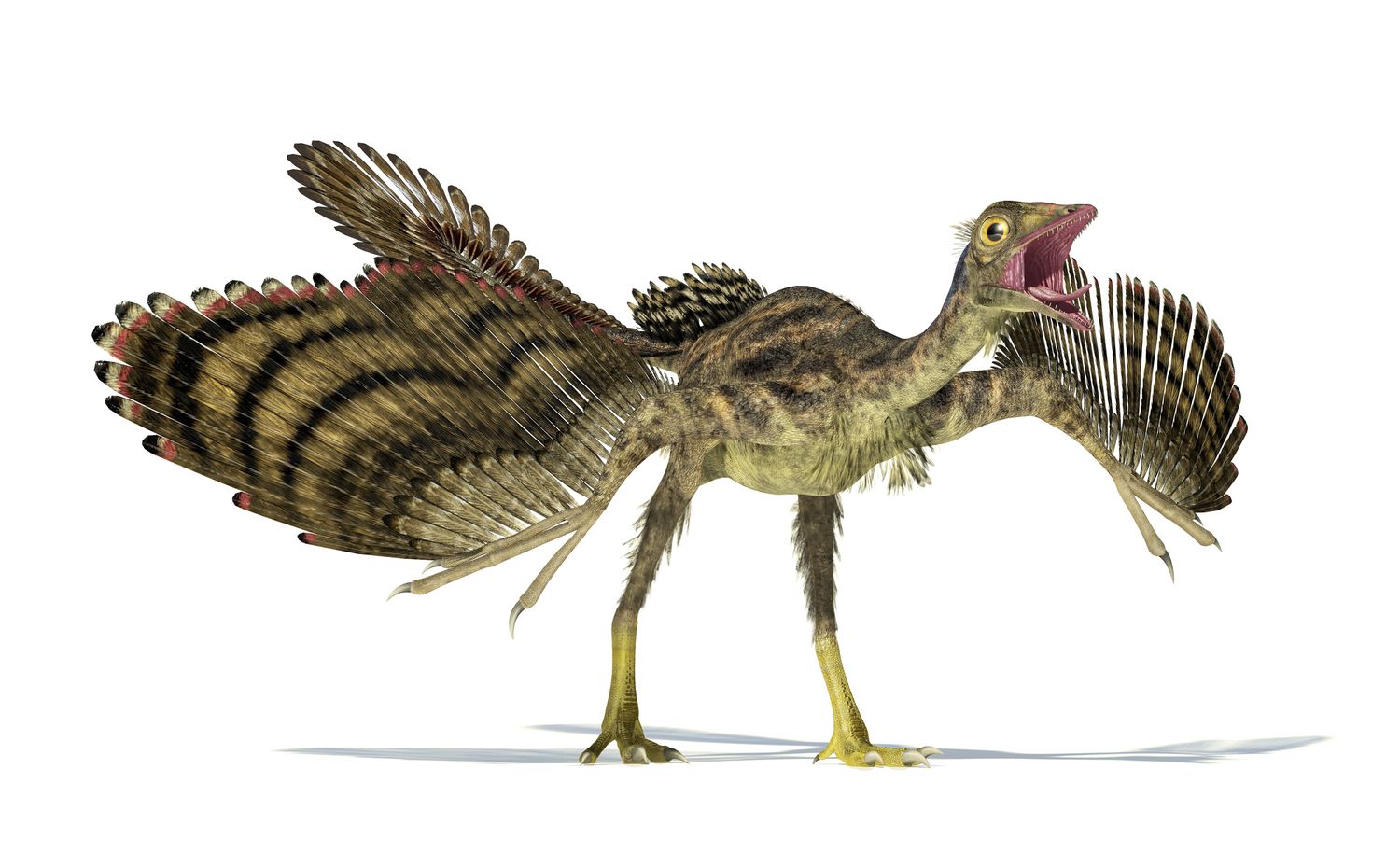

As mentioned in the previous slide, the evidence is now irrefutable that birds evolved from dinosaurs — but there are still many details about this process that remain unclear. For example, it is likely that birds evolved two or three times independently during the Mesozoic Era, but only one of these lineages survived the K/T Extinction 65 million years ago and continued gave birth to the ducks, pigeons and penguins we all know and love today. (And if you’re curious why modern birds aren’t dinosaur-sized, it all comes down to powered flight and the vagaries of evolution).
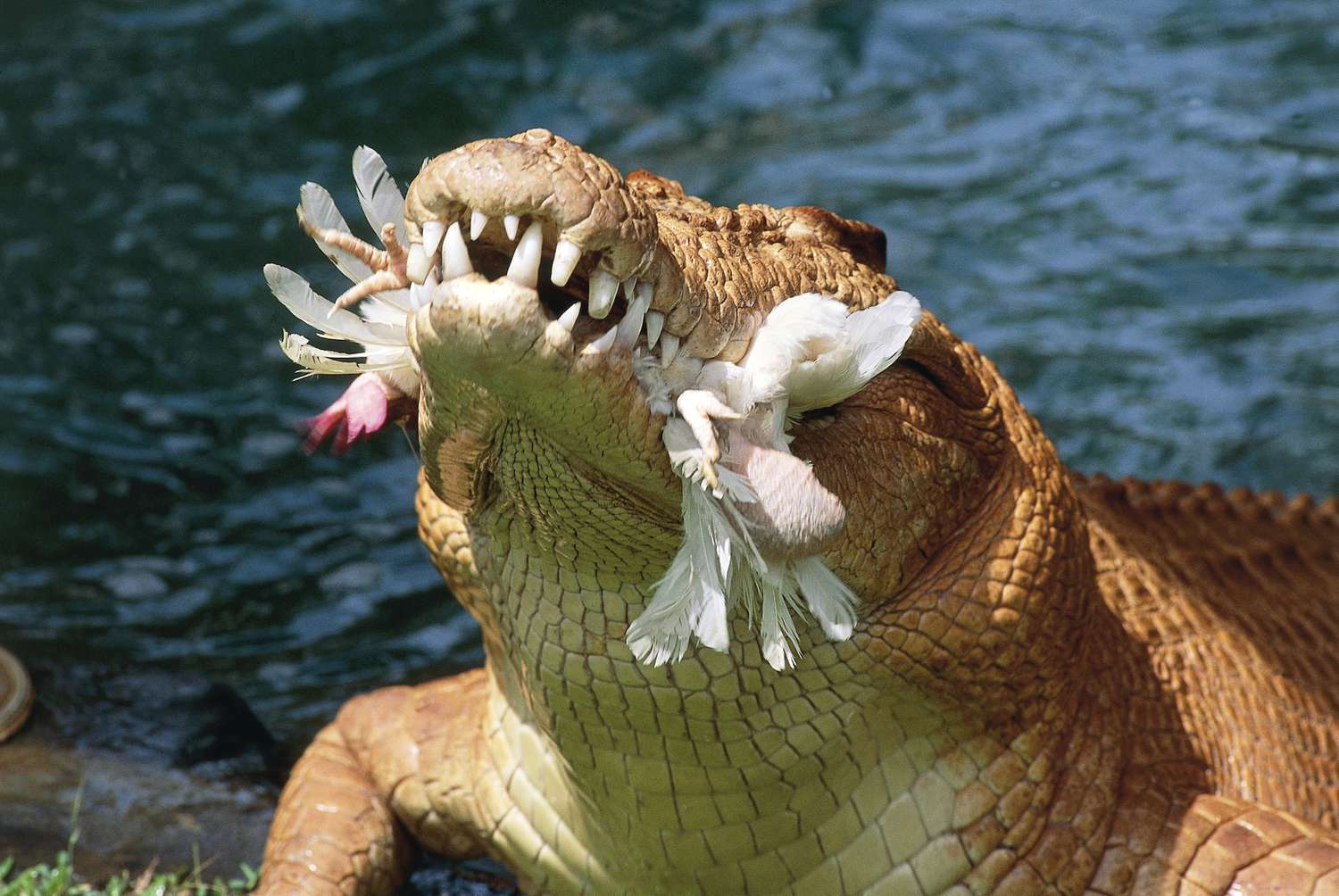

As vertebrates, birds are ultimately related to all other vertebrates that live or have ever lived on earth. But you might be surprised to learn that the family of vertebrates to which modern birds are most closely related is the crocodile, which evolved, like the dinosaurs, from a population of archosaur reptiles in the late Triassic period. . Dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and marine reptiles were all wiped out in the K/T Extinction Event, but crocodiles somehow survived (and will happily eat any bird, no matter how related). close or not, perched on their toothy snouts).
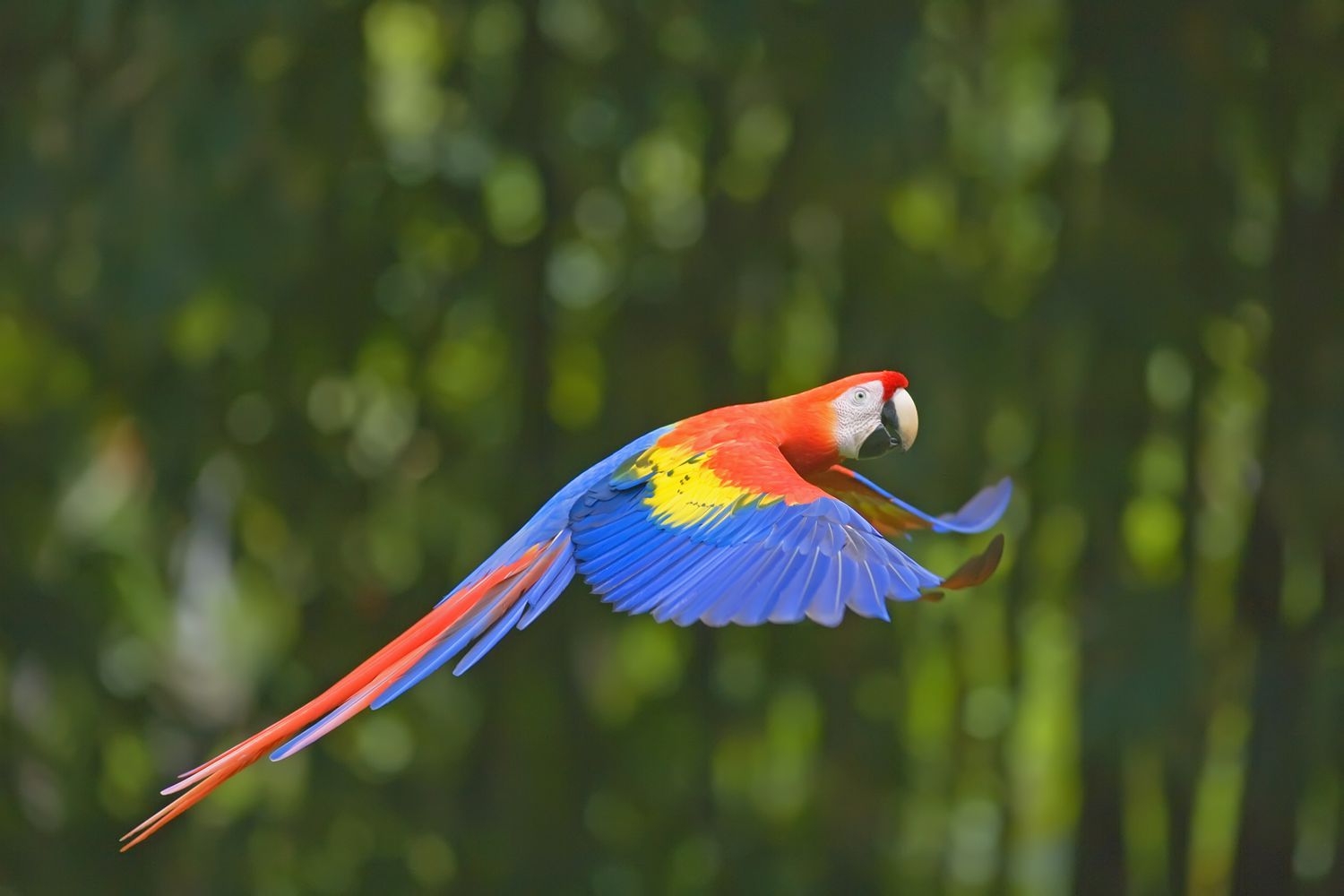

One thing you may notice about birds, especially finches, is that they are quite small – meaning they need a reliable way to locate each other during mating season. For this reason, perching birds have developed a variety of complex songs, trills and whistles, with which they can attract others of their kind in dense forest canopies, where they are virtually invisible. image. The bright colors of some birds also have a signaling function, often to assert dominance over other males or to demonstrate fertility.
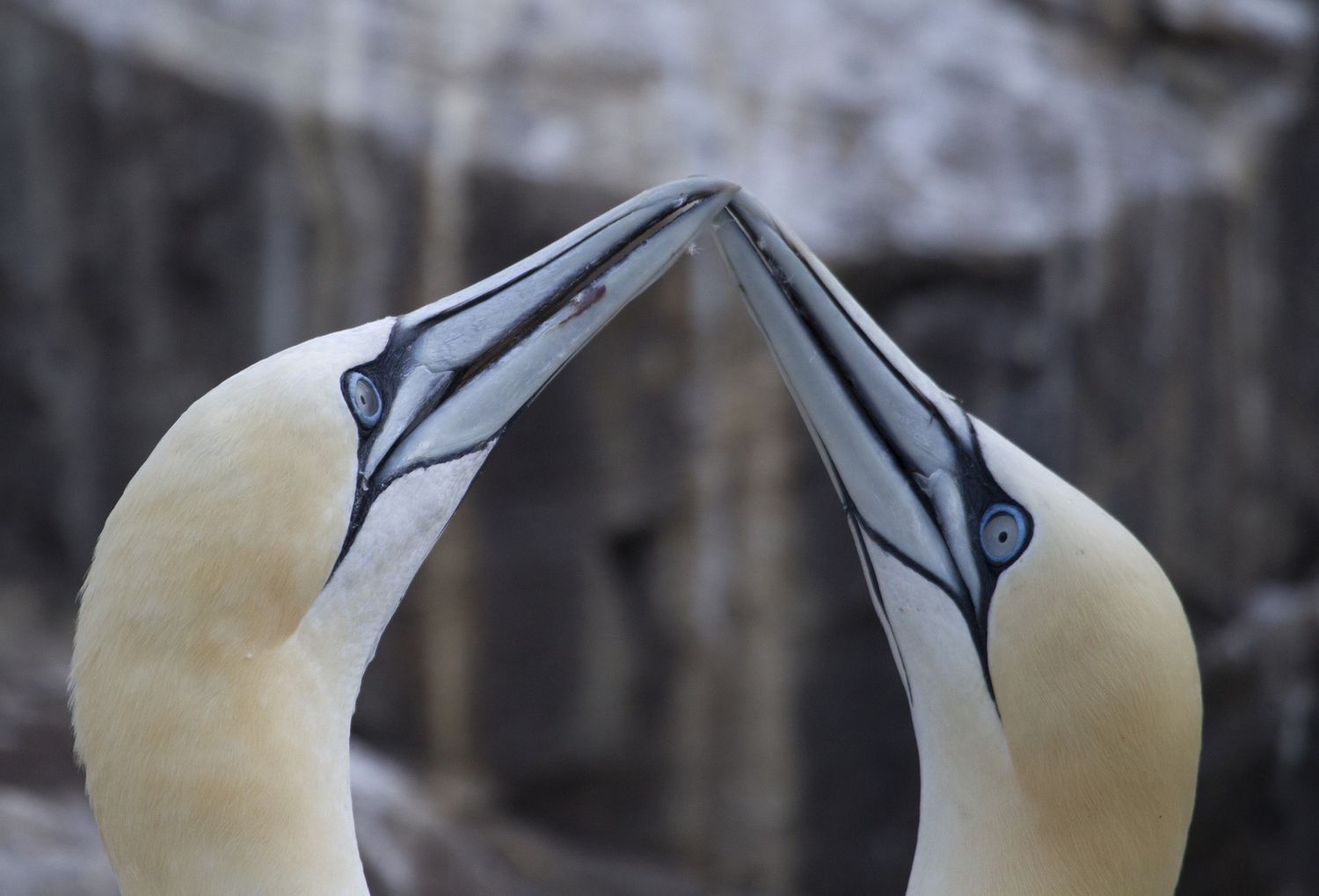

The word “monogamy” has different meanings in the animal world than it does in humans. In the case of birds, that means males and females of most species pair up for a breeding season, copulate and then raise their young – at which point they are free to find another mate for the next breeding season. However, some birds remain monogamous until the male or female dies, and some female birds have a little trick they can use in an emergency – they can save stores the male’s sperm and uses it to fertilize their eggs, for up to 100,000 times. three months.
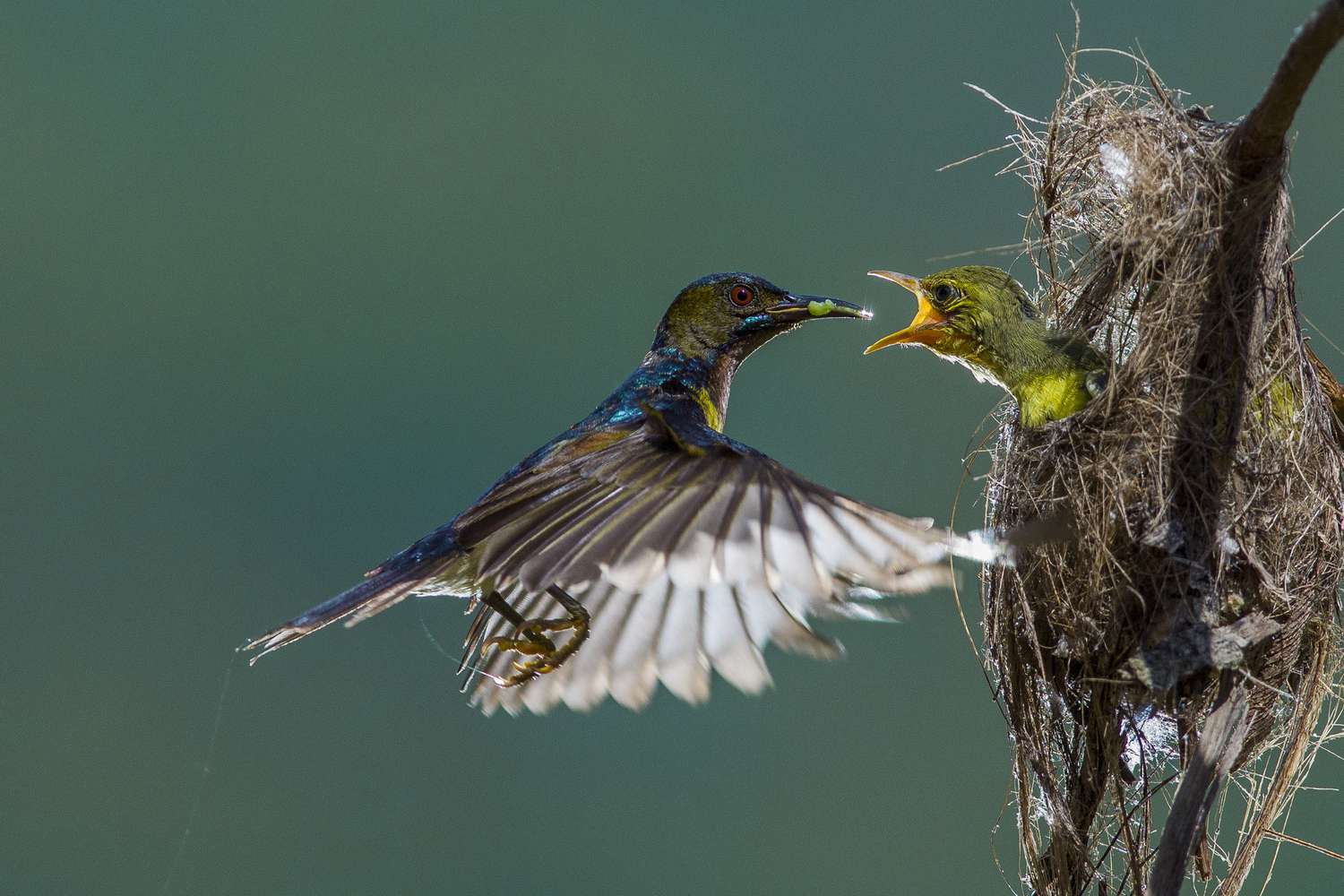

There are many different parenting styles across the bird kingdom. In some species, both parents incubate the eggs; In some places, only one parent cares for the young; and in other species, no parental care is required (for example, the Australian mallee lays its eggs in rotting vegetation, which provides a natural source of heat, and the young are completely independent once hatched. bloom). And we won’t even mention exceptions like cuckoos, which lay their eggs in other birds’ nests and leave the incubation, brooding, and feeding process to complete strangers.
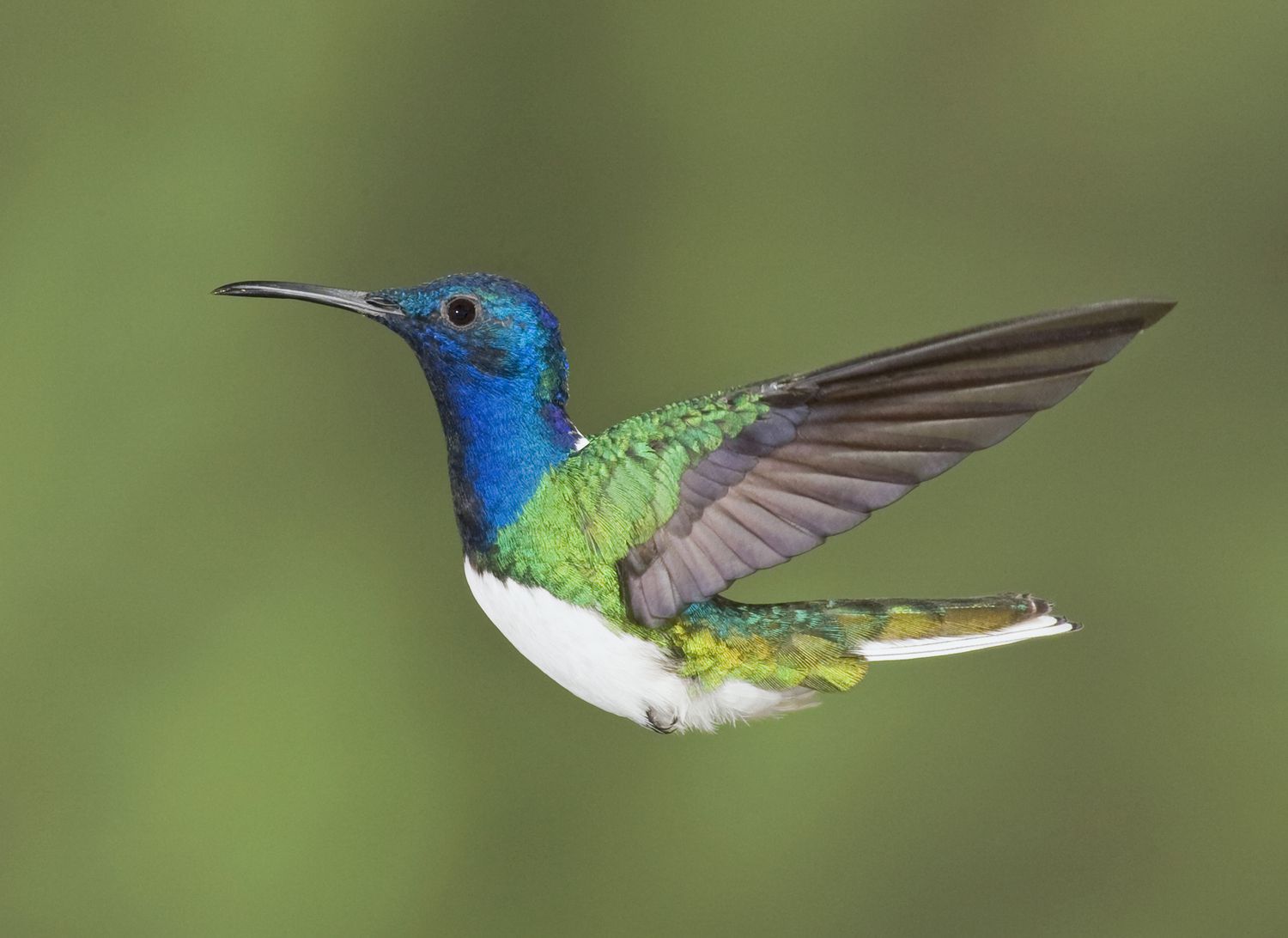

As a general rule, the smaller the endothermic (warm-blooded) animal, the higher its metabolic rate – and one of the best indicators of an animal’s metabolic rate is its heart rate. You might think that the chicken is just sitting there, doing nothing special, but actually its heart beats about 250 beats per minute, while a resting hummingbird’s heart rate measures more than 600 beats per minute. By comparison, a healthy domestic cat has a resting heart rate between 150 and 200 bpm, while an adult’s resting heart rate ranges around 100 bpm.
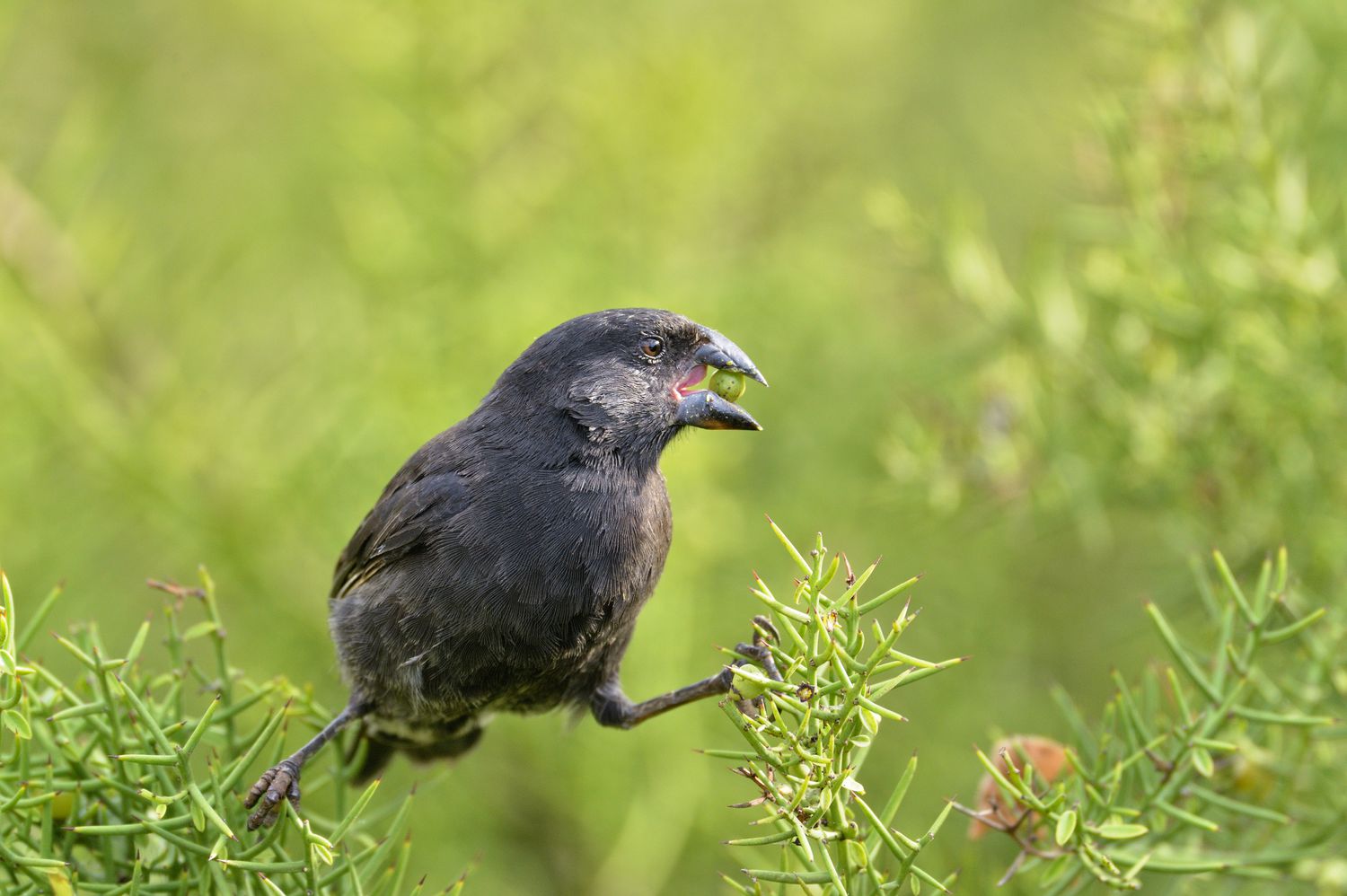

When Charles Darwin formulated his theory of natural selection in the early 19th century, he conducted extensive research on finches in the Galapagos Islands. He discovered that finches on different islands varied considerably in the size and shape of their beaks; it is clear that they have adapted to their individual habitats, but it is also clear that they all descend from a common ancestor that arrived in the Galapagos thousands of years ago. The only way nature could achieve this feat is by evolution through natural selection, as Darwin proposed in his groundbreaking book On the Origin of Species .